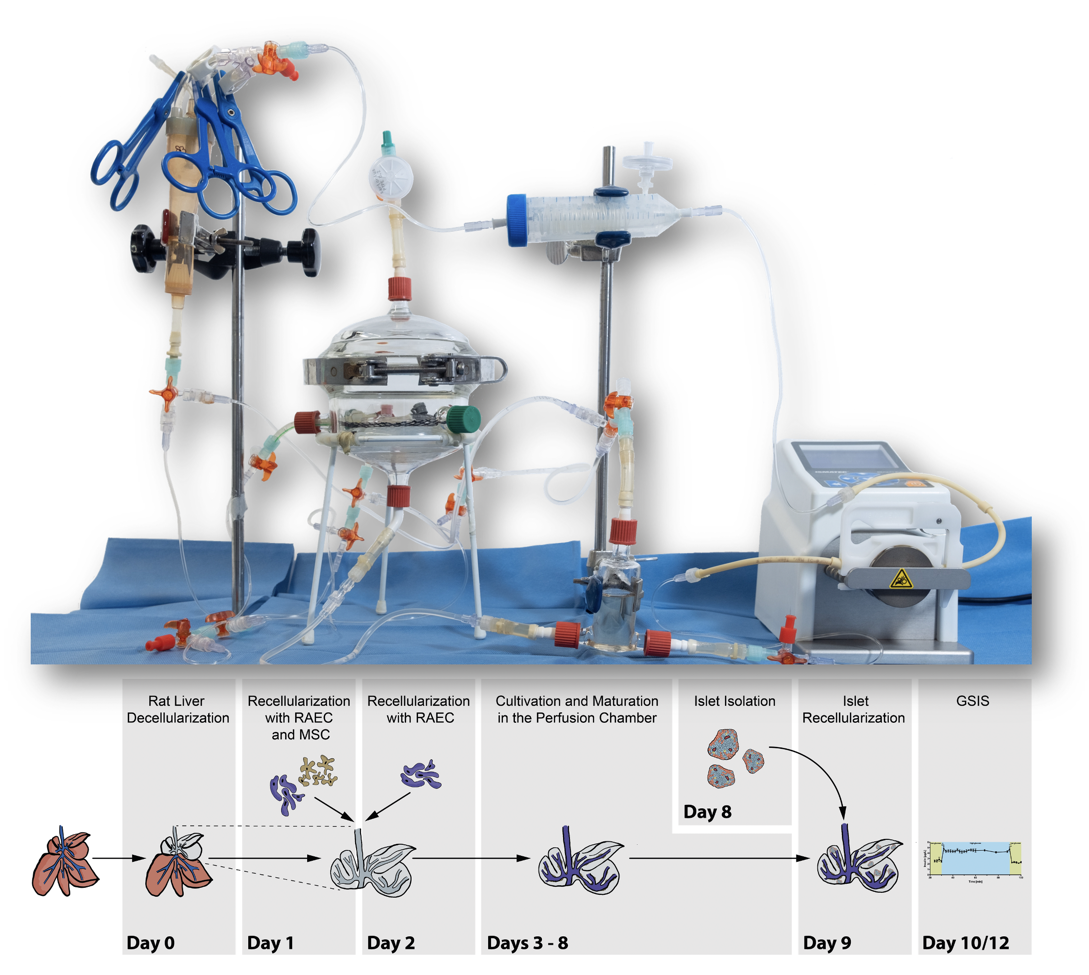
Recellularization of decellularized bovine carotid arteries

Many patients suffering from peripheral arterial disease (PAD) are dependent on bypass surgery. However, in some patients no suitable replacements (i.e. autologous or prosthetic bypass grafts) are available. Advances have been made to develop autologous tissue engineered vascular grafts (TEVG) using endothelial colony forming cells (ECFC) obtained by peripheral blood draw in large animal trials. Clinical translation of this technique, however, still requires additional data for usability of isolated ECFC from high cardiovascular risk patients.
Bovine carotid arteries (BCA) were decellularized using a combined SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) -free mechanical-osmotic-enzymatic-detergent approach to show the feasibility of xenogenous vessel decellularization. Decellularized BCA chips were seeded with human ECFC, isolated from a high cardiovascular risk patient group, suffering from diabetes, hypertension and/or chronic renal failure. ECFC were cultured alone or in coculture with rat or human mesenchymal stromal cells (rMSC/hMSC). Decellularized BCA chips were evaluated for biochemical, histological and mechanical properties. Successful isolation of ECFC and recellularization capabilities were analyzed by histology.
Decellularized BCA showed retained extracellular matrix (ECM) composition and mechanical properties upon cell removal. Isolation of ECFC from the intended target group was successfully performed (80% isolation efficiency). Isolated cells showed a typical ECFC-phenotype. Upon recellularization, co-seeding of patient-isolated ECFC with rMSC/hMSC and further incubation was successful for 14 (n = 9) and 23 (n = 5) days. Reendothelialization (rMSC) and partial reendothelialization (hMSC) was achieved. Seeded cells were CD31 and vWF positive, however, human cells were detectable for up to 14 days in xenogenic cell-culture only. Seeding of ECFC without rMSC was not successful.
Using our refined decellularization process we generated easily obtainable TEVG with retained ECM- and mechanical quality, serving as a platform to develop small-diameter (< 6 mm) TEVG. ECFC isolation from the cardiovascular risk target group is possible and sufficient. Survival of diabetic ECFC appears to be highly dependent on perivascular support by rMSC/hMSC under static conditions. ECFC survival was limited to 14 days post seeding.
Authors are N. Seiffert, P. Tang, E. Keshi, A. Reutzel-Selke, S. Moosburner, H. Everwien, D. Wulsten, H. Napierala, J. Pratschke, I.M. Sauer, K. Hillebrandt, and B. Struecker.
J Biol Eng 15, 15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13036-021-00266-5