BMBF funds KIARA
With the programme "AI-based assistance systems for process-accompanying health applications", the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) is funding innovative research and development work on interactive assistance systems that support processes in clinical health care using artificial intelligence methods.
Together with the partners Gebrüder Martin GmbH & Co. KG, Tuttlingen, HFC Human-Factors-Consult GmbH, Berlin and the Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications Heinrich-Hertz-Institut (HHI), Berlin, we successfully applied with the project "AI-based recording of work processes in the operating theatre for the automated compilation of the operating theatre report" (KIARA).
Together with the partners Gebrüder Martin GmbH & Co. KG, Tuttlingen, HFC Human-Factors-Consult GmbH, Berlin and the Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications Heinrich-Hertz-Institut (HHI), Berlin, we successfully applied with the project "AI-based recording of work processes in the operating theatre for the automated compilation of the operating theatre report" (KIARA).
Operating theatre reports document all relevant information during surgical interventions. They serve to ensure therapeutic safety and accountability and as proof of performance. The preparation of the OR report is time-consuming and ties up valuable working time – time that is then not available for the treatment of patients.
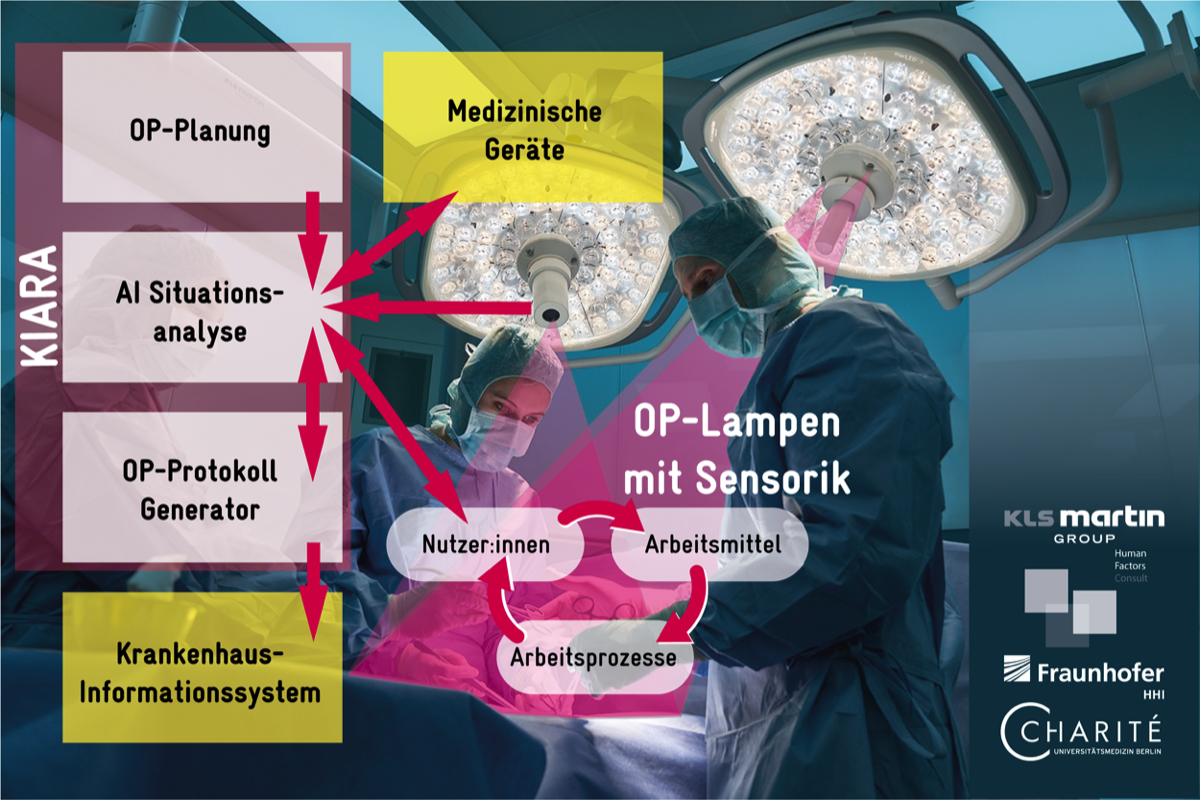
In the KIARA project, we are working on a system that automatically drafts operating theatre reports. The KIARA system is intended to relieve medical staff: it documents operating theatre activities and creates a draft of the report, which then only needs to be checked, completed and approved. The system works via cameras integrated into operating theatre lamps. Their image data is then analysed with the help of artificial intelligence to recognise and record objects, people and all operating theatre activities. The ambitious system is to be developed and tested in a user-centred manner for procedures in the abdominal cavity and in oral and maxillofacial surgery.
KIARA is intended to continuously learn through human feedback and to simplify clinical processes for the benefit of medical staff by automating the creation of operating theatre reports. The system can also be applied to other operating theatre areas in the future.
The project has a financial volume of € 2.16 million.
The kick-off meeting took place on 16.09.2022 at the Charité.